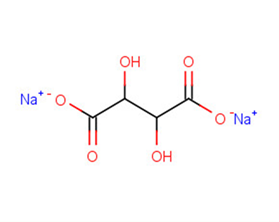
Sodium Tartrate
CAS No. 868-18-8
Sodium Tartrate( —— )
Catalog No. M20056 CAS No. 868-18-8
Sodium Tartrate is a food additive used as an emulsifier and binding agent in food products.
Purity : >98% (HPLC)
 COA
COA
 Datasheet
Datasheet
 HNMR
HNMR
 HPLC
HPLC
 MSDS
MSDS
 Handing Instructions
Handing Instructions
| Size | Price / USD | Stock | Quantity |
| 10MG | 40 | Get Quote |


|
| 25MG | 80 | Get Quote |


|
| 50MG | 131 | Get Quote |


|
| 100MG | 209 | Get Quote |


|
| 200MG | 314 | Get Quote |


|
| 500MG | 538 | Get Quote |


|
| 1G | Get Quote | Get Quote |


|
Biological Information
-
Product NameSodium Tartrate
-
NoteResearch use only, not for human use.
-
Brief DescriptionSodium Tartrate is a food additive used as an emulsifier and binding agent in food products.
-
DescriptionSodium Tartrate is a food additive used as an emulsifier and binding agent in food products.
-
In Vitro——
-
In Vivo——
-
Synonyms——
-
PathwayOthers
-
TargetOther Targets
-
RecptorOthers
-
Research Area——
-
Indication——
Chemical Information
-
CAS Number868-18-8
-
Formula Weight194.05
-
Molecular FormulaC4H4Na2O6
-
Purity>98% (HPLC)
-
SolubilityDMSO:10 mM
-
SMILES[Na+].[Na+].OC(C(O)C([O-])=O)C([O-])=O
-
Chemical Name——
Shipping & Storage Information
-
Storage(-20℃)
-
ShippingWith Ice Pack
-
Stability≥ 2 years
Reference
1.Zhao Y. Yuan H. Zhang X. & Yang J. (2018). A stimuli-responsive fluorescence platform for simultaneous determination of d -isoascorbic acid and Tartaric acid based on Maillard reaction product.?Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular And Biomolecular Spectroscopy?196 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2018.01.079
molnova catalog



related products
-
SIVmac239-2
SIVmac239-2
-
Methyl 4-bromopyrrol...
Methyl 4-bromopyrrole-2-carboxylate is a marine derived natural products found in Lissodendoryx sp.
-
Corydaline
Corydaline, an isoquinoline alkaloid, is one of the major active constituents in a new prokinetic botanical agent.



 Cart
Cart
 sales@molnova.com
sales@molnova.com


